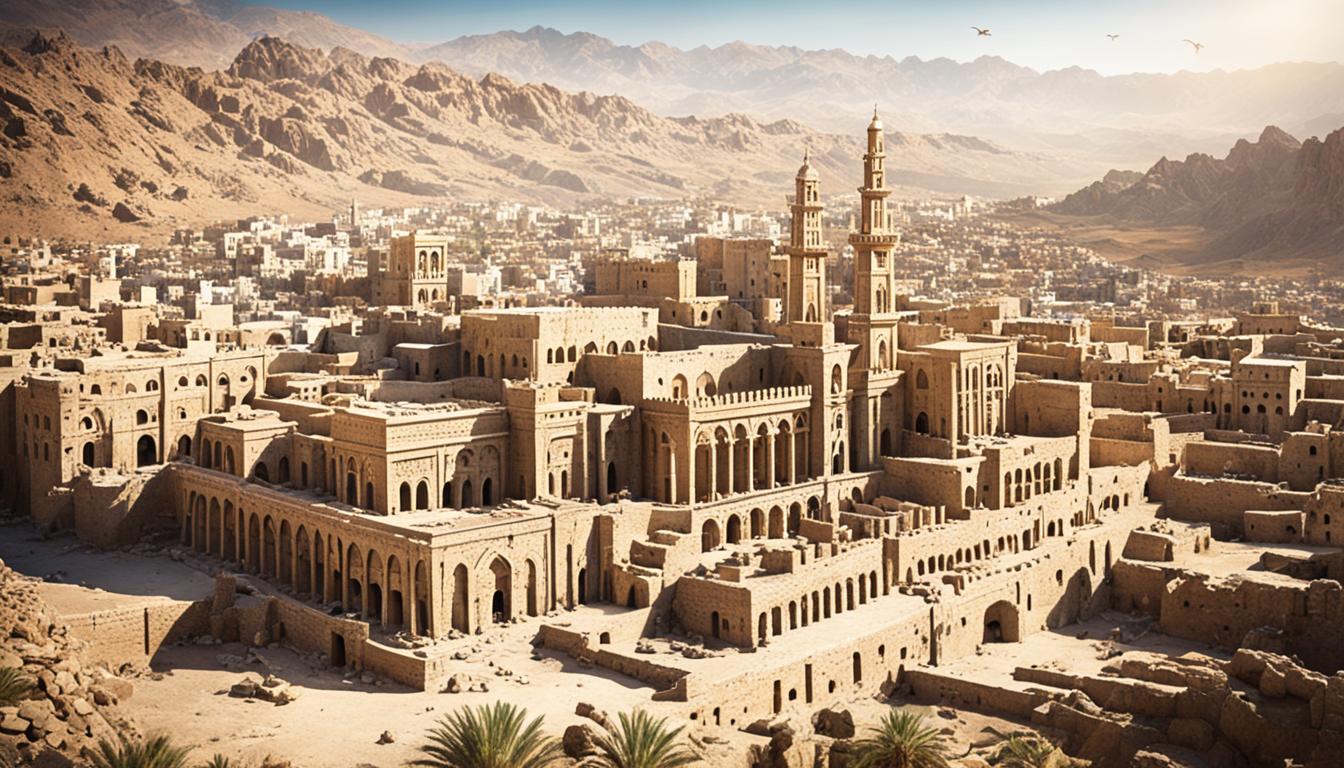
Imagine a city that has stood the test of time, where the echo of ancient civilizations whispers through the winding streets. Welcome to Sana’a, Yemen, a captivating hub of Arabian Peninsula archaeology. This ancient metropolis, nestled in a mountain valley at an altitude of 2,200 meters, has been continuously inhabited for over 2,500 years, bearing witness to the ebb and flow of empires and the spread of Islam across the region.
Sana’a’s rich history is a testament to the enduring legacy of the Arabian Peninsula, where the remnants of pre-Islamic and Islamic cultures converge in a tapestry of architectural wonders and archaeological treasures. From the well-preserved Islamic architecture that defines the city’s skyline to the trove of historical artifacts housed in its museums, Sana’a offers a window into the captivating story of Yemen’s past.
Key Takeaways
- Sana’a, Yemen, has been continuously inhabited for over 2,500 years, making it a crucial center of Arabian Peninsula archaeology.
- The city is renowned for its well-preserved Islamic architecture, including 103 mosques, 14 hammams (public baths), and over 6,000 houses built before the 11th century.
- Sana’a’s rich history spans from the pre-Islamic era to the spread of Islam in the 7th and 8th centuries, offering a glimpse into the enduring legacy of the Arabian Peninsula.
- The city’s architectural wonders and archaeological treasures provide a window into Yemen’s captivating past.
- Sana’a’s strategic location in a mountain valley at an altitude of 2,200 meters has contributed to its long-standing importance as a center of regional history and culture.
The Ancient City of Sana’a: A Marvel of Islamic Architecture
Sana’a, the vibrant capital of Yemen, boasts a captivating architectural landscape that has stood the test of time. The city’s Old City is a testament to the remarkable Sana’a Architecture and the enduring Islamic Architectural Heritage of the region.
At the heart of Sana’a’s architectural wonders are the towering Rammed Earth Buildings and Traditional Yemeni Structures, which rise several stories above the stone-built ground floors. These structures are adorned with intricate geometric patterns of fired bricks and white gypsum, blending seamlessly with the nearby ochre-hued mountains.
Mosques, Hammams, and Caravanserais
Sana’a’s architectural tapestry is further enriched by the presence of majestic mosques, tranquil hammams (public baths), and bustling caravanserais (inns). The city’s skyline is punctuated by the soaring minarets of these iconic structures, while lush green bustans (gardens) are scattered between the densely packed houses, showcasing the city’s commitment to harmonizing its built environment with nature.

The ancient city of Sana’a stands as a testament to the enduring brilliance of Islamic Architectural Heritage, where the past and present coexist in a captivating blend of history, culture, and timeless design.
Yemen: Arabian Peninsula Archaeology Sana’a Yemen
The ancient city of Sana’a in Yemen has played a crucial role in the archaeology of the Arabian Peninsula, with its history spanning over 2,500 years. This historic city’s strategic location and its emergence as a center of trade and religious significance have made it a vital site for understanding the development of ancient civilizations in the region.
Sana’a’s archaeological significance is a testament to the rich history of Yemen and the ancient Arabian civilizations that flourished in this part of the world. The city’s well-preserved architectural marvels, such as its rammed earth and burnt brick towers, mosques, hammams, and caravanserais, offer a glimpse into the sophisticated urban planning and construction techniques of the past.

Archaeologists have uncovered numerous artifacts and ruins in Sana’a, providing valuable insights into the cultural, economic, and social dynamics of the region. The city’s role as a hub for trade and religious activities has further cemented its significance as a crucial site for understanding the evolution of ancient Arabian civilizations.
The ancient city of Sana’a, with its rich heritage and archaeological treasures, continues to captivate scholars and visitors alike, offering a unique window into the past and the enduring legacy of Yemen’s Arabian Peninsula archaeology.
The Great Mosque of Sana’a: Cradle of Islamic Civilization
The Great Mosque of Sana’a stands as a remarkable testament to the city’s pivotal role in the early spread of Islam. According to tradition, this architectural marvel was constructed during the lifetime of the Prophet Muhammad, making it one of the earliest mosques built outside the holy cities of Mecca and Medina. Its very existence underscores Sana’a’s enduring significance in the religious heritage of the Arabian Peninsula.
Architectural Splendor of Early Islam
The Great Mosque of Sana’a is a stunning example of the grandeur that characterized early Islamic architecture. Its intricate decorations, multiple prayer halls, and imposing presence reflect the cultural and artistic achievements of the nascent Islamic civilization. The mosque’s architectural splendor not only showcases the region’s religious devotion but also reveals the ingenuity and skill of its master builders during this formative period of Islamic history.
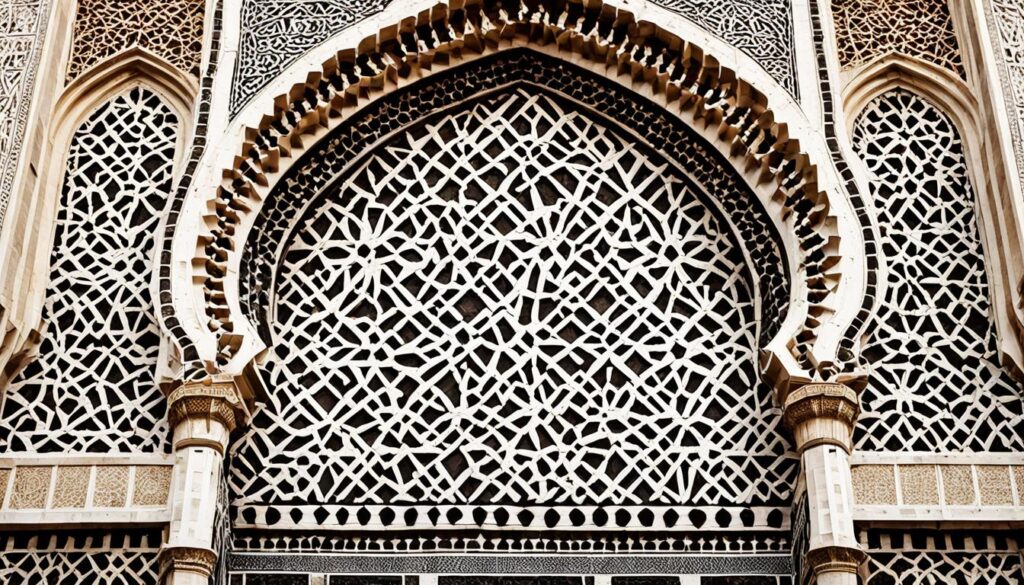
Construction During the Prophet’s Lifetime
According to the revered tradition, the Great Mosque of Sana’a was constructed during the lifetime of the Prophet Muhammad, making it one of the earliest mosques built outside the holy cities. This remarkable fact underscores Sana’a’s significance as a center of early Islamic civilization, where the faith took root and flourished in the centuries following the Prophet’s time. The mosque’s enduring presence serves as a testament to the city’s pivotal role in the spread of Islam throughout the Arabian Peninsula.
The National Museum of Yemen: Preserving a Rich Heritage
In the heart of Sana’a, the National Museum of Yemen plays a vital role in safeguarding the country’s vast archaeological and cultural legacy. Established in 1971, this esteemed institution houses a remarkable collection of artifacts from the Sabaean, Himyarite, and Islamic eras, offering visitors a captivating glimpse into the diverse history of Yemen and the Arabian Peninsula.
With over 30,000 pieces in its extensive holdings, the National Museum of Yemen serves as a testament to the region’s rich cultural heritage. Visitors can explore a vast array of archaeological artifacts, from intricate pottery and metalwork to ancient inscriptions and architectural fragments, all meticulously preserved and displayed to educate and inspire.
The museum’s dedication to the preservation of Yemeni cultural treasures extends beyond its walls, as it plays a crucial role in advocating for the protection of the country’s archaeological sites and promoting Yemeni cultural preservation efforts. Through its educational programs, research initiatives, and collaborative partnerships, the National Museum of Yemen continues to be a beacon of knowledge and a custodian of Yemen’s remarkable past.
Archaeological Sites of Ancient Yemen
Yemen, the land of ancient civilizations, is a treasure trove of archaeological marvels that offer a glimpse into the region’s rich Yemeni Archaeology and the legacy of the Ancient Arabian Kingdoms. Beyond the historic city of Sana’a, two sites in particular stand out as beacons of this captivating past: Marib and Timna.
Marib: Fabled City of the Queen of Sheba
Marib, the legendary capital of the ancient Kingdom of Sheba, is a testament to the engineering prowess of this powerful civilization. The site features the remains of impressive temples, dams, and other structures that bear witness to their technological achievements. Visitors can explore the remnants of the iconic Dam of Marib, an engineering marvel that once controlled the flow of water in the region, as well as the ruins of the ancient Awwam Temple, dedicated to the moon god Almaqah.
Timna: Remnants of the Minaean Kingdom
Timna, another remarkable archaeological site in Yemen, preserves the remnants of the Minaean Kingdom, one of the major trading powers in the Ancient Arabian Kingdoms during the pre-Islamic era. Visitors can wander through the ruins of ancient fortresses, temples, and settlements, gaining a deeper understanding of the Minaean civilization and their critical role in the regional trade networks that connected Yemen to the Mediterranean world.

Preserving Yemen’s Cultural Treasures
The preservation of Yemen’s rich cultural heritage has faced significant challenges in recent years, as the country has been embroiled in a prolonged conflict. The ancient city of Sana’a, a UNESCO World Heritage site renowned for its stunning Islamic architecture, has been particularly vulnerable to the effects of war and instability.
The National Museum of Yemen, once a vital repository for the country’s archaeological wonders, was even forced to close its doors for a time due to the ongoing unrest. Despite these setbacks, organizations like the General Organization for the Preservation of the Historic Cities of Yemen (GOPHCY) have remained steadfast in their efforts to safeguard these invaluable Yemeni cultural treasures.
Challenges of War and Instability
The threats to Yemen’s archaeology and cultural heritage are multifaceted, ranging from the direct damage caused by armed conflicts to the long-term neglect and looting that can occur during periods of instability. The Old City of Sana’a, with its rammed earth and burnt brick towers, has been particularly susceptible to the effects of the conflict, with damage to historic buildings and the risk of irreparable loss.
Despite these daunting challenges, the determination to preserve Yemen’s cultural legacy remains strong. Ongoing restoration and conservation efforts, coupled with international support and collaboration, offer hope that these Yemeni cultural treasures can be protected for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.
The Socotra Archipelago: A Natural Wonder
Beyond Yemen’s rich archaeological legacy lies the stunning Socotra Archipelago, a remote and isolated group of islands that have been designated a UNESCO World Heritage site. These islands, located in the Gulf of Aden, are renowned for their unique and diverse flora and fauna, with a large percentage of endemic species found nowhere else on Earth. The archipelago’s natural beauty and fragile ecosystem make it a crucial part of Yemen’s Yemeni Natural Heritage that requires careful preservation.
The Socotra Archipelago is a true natural wonder, boasting an exceptional Biodiversity that has captured the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts worldwide. From the iconic dragon’s blood trees to the vibrant coral reefs, the islands’ unique landscapes and ecosystems are a testament to the incredible adaptability and resilience of life on the planet. Protecting this precious natural heritage is not only a matter of preserving Yemen’s environmental legacy but also safeguarding the delicate balance of the Earth’s biodiversity.
The Ghumdan Palace: Architectural Gem of Sana’a
Nestled in the heart of Sana’a, the capital of Yemen, stands the Ghumdan Palace, a magnificent testament to the architectural prowess of the region. This iconic landmark, dating back to the 3rd century AD, was once the seat of power for the ancient Kingdom of Saba and later the Himyarite Kingdom, making it a true icon of Yemeni royal architecture.
While much of the original Ghumdan Palace has been lost to the ravages of time, the remaining ruins and reconstructed elements offer a captivating glimpse into the grandeur and sophistication that once defined Yemeni architecture during its golden age. The palace’s towering rammed earth and burnt brick towers, intricate archways, and ornate decorative elements are a testament to the ingenuity and craftsmanship of the region’s master builders.
The Ghumdan Palace, with its rich history and architectural splendor, stands as a symbol of Sana’a’s enduring legacy as a hub of Yemeni culture and heritage. Visitors to this historic site can immerse themselves in the fascinating stories of the past and marvel at the enduring beauty of Yemeni royal architecture, making it a must-visit destination for anyone exploring the wonders of the Arabian Peninsula.
Zabid: Renowned Center of Islamic Learning
Nestled within Yemen’s rich cultural tapestry, the historic city of Zabid has long been revered as a hub of Islamic scholarship. Once home to the prestigious Zabid University during the Abbasid era, this ancient city attracted scholars from across the Muslim world, cementing its status as a renowned center of learning and religious significance.
Zabid’s well-preserved architectural marvels, including its mosques and traditional houses, continue to reflect the depth of Yemeni cultural heritage. These structures serve as tangible reminders of the city’s illustrious past, when it stood as a beacon of Islamic scholarship and intellectual discourse.
Today, Zabid’s legacy endures, offering visitors a unique glimpse into the region’s rich history and the pivotal role it played in shaping the cultural and religious landscape of the Arabian Peninsula. As a testament to the resilience of Yemeni cultural heritage, Zabid’s enduring significance continues to captivate and inspire those who seek to unravel the mysteries of this remarkable city.
Conclusion
Yemen’s rich archaeological and cultural heritage, exemplified by the ancient city of Sana’a and other significant sites, offers a captivating glimpse into the region’s complex and multifaceted past. From the pre-Islamic civilizations to the spread of Islam and the subsequent development of unique architectural and scholarly traditions, Yemen’s legacy continues to fascinate researchers and visitors alike. However, the preservation of these invaluable treasures remains a significant challenge, particularly in the face of ongoing conflicts and instability.
Sustained efforts by Yemeni and international organizations are crucial to ensuring that this remarkable Yemen Archaeology and Arabian Peninsula History are safeguarded for future generations to explore and appreciate. Through dedicated preservation initiatives and collaborative efforts, the Preserving Cultural Heritage of Yemen can be protected, allowing the world to continue to marvel at the architectural wonders and uncover the mysteries that lie within this ancient land.
As we move forward, the importance of preserving Yemen’s cultural legacy cannot be overstated. By protecting and promoting this heritage, we not only honor the past but also pave the way for a deeper understanding and appreciation of the region’s rich tapestry of history and culture.
Source Links
- Old City of Sana'a – https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/385/
- National Museum of Yemen – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Museum_of_Yemen
- DAI – Library – https://www.dainst.org/en/departments/orient-department/about-us/branches-and-research-units/sanaa-branch/infrastructures/library


